SCN ray-tracing format
Original by António Costa
- The SCN (SCeNe format)
was invented to replace a very simple format called SFF for the Rtrace
ray-tracer. It is
used to describe environments (geometry, topology, attributes, etc.) that are
processed by programs called ray-tracers, although it can be used by other
programs.
- The RTrace ray-tracer uses a
very simplistic format (its only advantage is the simplicity!). It only reads
numbers (and strings for file names), but its syntax is very rigid. To avoid
this, I decided to create a much more elaborated, easy to write and flexible
scene description format, which I called SCN.
- To avoid modifying the RTrace input code, a translator from SCN to SFF was
implemented as a separate program (Scn2Sff), meant to be
used as a preprocessor for RTrace (in UNIX and DOS, these two programs can be
used in a pipe like scn2sff | rtrace).
- The SCN format does not have sections like SFF, RTrace's input format, and it
supports comments and even other preprocessor constructs (for example,
cpp and m4 for UNIX and DOS). Another important difference is
that it has default values for some scene parameters, which means that they do
not have to be specified at all.
- The basic components of SCN are:
- comment - they start anywhere on the line with some special
character like ; # or % and terminate in the end of line.
- integer - any valid integer number, an integer expression
inside parenthesis or the result of the int() function.
Examples:
0
1
-2
(1 + 2) ; 3
int(10 / 3) ; 3
- real - any valid integer or real number, a real expression
inside parenthesis or the result of any real-valued function like
sin(), cos(), etc. Examples:
0.0
1.5
(1 + 2.1) ; 3.1
log(2) ; 0.6931
- color - a triplet of RGB reals between 0 and 1. In certain
cases, the RGB reals may be bigger than 1 or negative
(color_extended). It is also possible to use names that
represent the RGB values or the mono keyword followed by just
one real. Examples:
0 0 0 ; black
1 1 1 ; white
1 0 0 ; red
white
red
mono 0.5 ; medium gray
- point - a triplet of reals representing X Y and Z values or
the result of any point-valued function like normvector(),
addvector(), etc. Examples:
0 0 0 ; world origin
10 5 1
1 (2 + 1) (10 * sin(0.1)) ; 1 3 0.0175
normvector(1.1 2.5 -2.3) ; 0.3081 0.7001 -0.6441
addvector(1 2 3, 4 5 6) ; 5 7 9
- vector - similar to a point, but cannot be equal to 0 0 0.
- filename - a set of characters (letters, digits and others)
with no blanks between. It is recommended to use only file names like
those of DOS.
- expression - anything inside parenthesis. An expression can
be integer or real. The expression operators are + - * / ^ and | .
Examples:
(1 + 2) ; 3
(1 - 2) ; -1
(1 * 2) ; 2
(1 / 2) ; 0.5
(1 ^ 2) ; 1.0
(5 | 3) ; 2
- function - there are many functions available. The
integer/real-valued with integer/real arguments are int(), sin(),
cos(), tan(), asin(), acos(), atan(), sqrt(), rtod (), dtor (), exp(),
log(), abs(), max() and min(). The dotvector()
function has two vector arguments and returns a real number. There are
also functions with point/vector arguments that return point/vector
quantities like normvector(), addvector(), diffvector(),
scalevector() and crossvector(). Examples:
tan(dtor(45)) ; 1.0
rtod(atan(1)) ; 45 degrees
log(exp(2)) ; 2
abs(-1.5) ; 1.5
max(0, 1) ; 1
dotvector(1 0 0, 0 1 0) ; 0.0
scalevector(1 0 0, 2) ; 2 0 0
scalevector(2 2 2, 1 2 3) ; 2 4 6
crossvector(1 0 0, 0 1 0) ; 0 0 1
- To specify viewing parameters one can use the following instructions:
- eye point - where the camera is (default is 5 0 0);
from can also be used.
- look point - where the target of the camera is (default 0 0
0); at can also be used.
- up vector - the camera vertical direction (default 0 1 0).
- fov real [real] - the horizontal/vertical fields of view
(default 22.5 degrees); angle can also be used. If there is just
one value, then both fields of view are equal.
- Examples:
eye 5 1 1
look 0 1 0 ; default up is 0 1 0
fov rtod(atan(320.0 / 200.0 * tan(dtor(15)))) 15 ; 23.21 15
- To specify the ambient and background colors, there are the following instructions:
- background color - the background color; default
light_blue_sky (approx. 0.1 0.5 0.7).
- ambient color - the ambient color (diffuse global lighting);
default 0.1 0.1 0.1 (dark gray).
- Examples:
background white
ambient mono 0.2
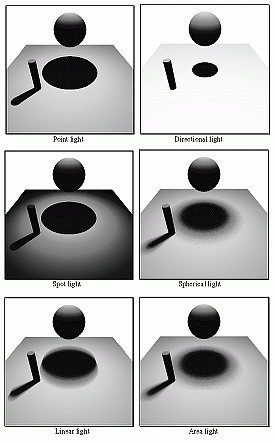
- To specify lights attributes, there are several instructions:
- light point point [color_extended] - this is a point light
that irradiates in any direction. If any of the color components is
negative, then there is no distance fall-off. Default color is white.
- light directional vector [color] - this is a light like the
Sun that irradiates along a direction, with no distance fall-off.
- light spot point vector color_extended [angle [factor]] -
this light illuminates inside a cone defined by the angle (default 45
degrees) with a transition that can be sharp (factor near 1) or smooth
(factor >> 1). The default value for factor is 1.
- light extended point color_extended radius samples - a
spherical light sampled samples2 rays.
- light linear point color_extended vector samples - a thin
linear light source defined by the vector and centered at given point.
It is sampled by samples rays.
- light planar point color_extended vector vector samples
samples - a kind of area light source defined by the two vectors
(the given point is at the center of the area). It is sampled by the
product of samples (8 by 8 is generally good).
- Examples:
light point 2 6 1 yellow
light directional -1 -1 -1 ; white
light spot 0 5 0 0 -1 0 red 30 2 ; smooth 30 degrees spot
light extended -3 5 3 green 0.5 8 ; 0.5 radius light sphere
light linear 1 8 3 white 0 0 2 32 ; white linear light
light planar 9 1 8 blue 1 0 0 0 0 1 8 8 ; blue square light
- Examples of the six light sources. The basic scene is:
eye 7 5 0
at 0 0
fov 30
background white
sphere surface matte mono 0.8 data 0 3 0 1
cylinder surface matte mono 0.7 data 2 0 2 2 2 2 0.2
box surface matte white data 0 0 0 5 0.01 5
light ...
- A surface is a non-geometric attribute that each object must have so
that it can be rendered. When a surface is defined in a certain scope, it
is considered the current surface and many objects may share it without
having to name it explicitly. There is even a default surface (surface
white mono 0.9 mono 0.1 3 0). A surface may have its special
attributes, which must appear immediately after the surface keyword, like:
- emitter - the objects using this surface behave like
emitters, ie, they have a constant shading, independent of the light
sources.
- noshadow - the objects using this surface do not have any
shadows.
- To specify surfaces, there are the following commands:
- surface color [diffusion specularity phong metalness
[transparency]] - phong and metalness are reals, the others are
colors. Defaults 0.9 0.9 0.9, 0.1 0.1 0.1, 3, 0 and 0.1 0.1 0.1; if
only transparency is omitted, then its default is 0 0 0.
- surface strauss color smoothness metalness [transparency] -
all are colors; default transparency is 0 0 0. This is an alternative
to the previous command that uses a more intuitive way of specifying
attributes.
- surface matte color - 100% diffuse surface.
- surface plastic color smoothness phong - plastic surface
(high diffusion, small specularity and phong factor).
- surface metal color smoothness phong - metallic surface
(small diffusion, high specularity and phong factor, maximum
metalness).
- surface dielectric color transparency refraction -
non-opaque surface (no diffusion, small specularity, large phong
factor and nometalness). Needs a refraction index.
- surface glass color transparency - transparent surface with
refraction index near 1.52 and similar to dielectric.
- refraction real - this specifies the current refraction index.
- Examples:
surface blue mono 0.7 mono 0.3 15 0.7 ; matte
surface strauss brown mono 0.9 mono 0.1 ; matte
surface matte red ; 100% matte
surface plastic beige mono 0.8 0.5 ; plastic
surface metal white mono 0.9 0.9 ; metallic
surface dielectric white mono 0.8 1.2 ; translucent
surface glass white mono 0.95 ; white glass
- The supported objects in SCN can be of two types. The objects of the
first type define a closed volume, while the others do not and must be
handled with care inside CSG operations (see the list primitive
bellow). Any object may inherit global attributes like surface, textures
and transformations or else define its private attributes using the data
keyword before its geometric information. It is also possible to group
several objects and make them share some attributes using the group
... ungroup keywords. Example:
transform none
surface matte white ; current surface
box ... ; white
group
surface matte red ; current surface inside block
transform rotate y 45 ... ; current transform inside block
sphere ... ; rotated, red
cone surface matte green data ... ; rotated, green
cube bump data ... ; rotated, red, bump texture
cylinder ... ; rotated, red
ungroup
prism ... ; white
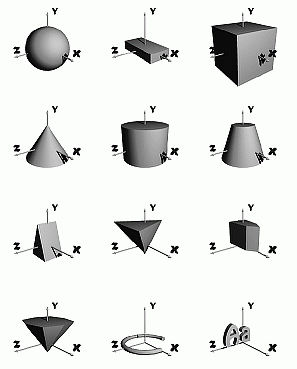
- The closed objects are:
- sphere [... data] center radius - a sphere.
- box [... data] center sizes - an axis aligned box.
- cube [... data] center size - an axis aligned cube.
- cone [... data] apex base base_radius - a cone.
- cylinder [... data] apex base radius - a cylinder.
- cone truncated [... data] apex apex_radius base base_radius
- truncated cone.
- wedge [... data] point point point depth - a wedge is
defined by a triangular face and an extrusion vector whose length is
depth; the face is defined counterclockwise and the vector points in
the Right Hand Rule direction (this convention is general in SCN).
- tetra [... data] point point point point - a general
tetrahedron (composed of four triangles).
- prism [... data] depth vertices point ... point - a prism
defined by a polygonal face and an extrusion vector similar to wedge.
- pyramid [... data] depth vertices point ... point - a
pyramid.
- torus [... data] out_radius in_radius start_angle end_angle
[out_samples in_samples] - a torus is centered in 0 0 0 and lies in
the XY plane (0 degrees is in the X axis direction and increases
counterclockwise). Actually, a torus is composed by a collection of
Phong triangles whose density is defined by out_samples
in_samples (default 16 8).
- text3d file [... data] filename - text primitives stored in
a file (high quality 3D letters, symbols, etc).
- Examples of closed objects:
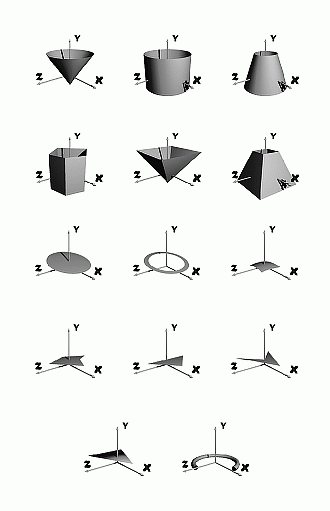
- The opened objects are:
- cone open [... data] apex base base_radius
- cylinder open [... data] apex base radius
- cone truncated open [... data] apex apex_radius base
base_radius
- prism open [... data] depth vertices point ... point
- pyramid open [... data] depth vertices point ... point
- pyramid truncated open [... data] depth apex_scale vertices
point ... point - this is an opened pyramid with the apex face
scaled by apex_scale in relation to its base face (0 is an opened
pyramid and 1 is a opened prism).
- disc [... data] center normal radius - a circle.
- ring [... data] center normal out_radius in_radius - a
circle with a hole.
- patch [... data] point ... point (12) - a bicubic patch is
defined by its corners and eight exterior points.
- patch file [... data] [point [point]] filename - a group of
patches stored in a file; first point defines a translation and second
a scaling.
- polygon [... data] vertices point ... point - polygon
without holes.
- polygon file [... data] [point [point]] filename - a group
of polygons stored in a file.
- triangle [... data] point point point
- quadrangle [... data] point point point point - four-sided
polygon.
- triangle normal [... data] point vector point vector point
vector - a triangle with normals in its vertices (also called Phong
triangles).
- triangle normal file [... data] [point [point]] filename - a
group of Phong triangles stored in a file.
- triangle general [... data] point vector point vector point
vector surface surface surface - a triangle with normals and
surfaces in its vertices. It is similar to a triangle normal, but
allows the interpolation of any (or all) of the surface parameters
inside itself.
- triangle general file [... data] [point [point]] filename -
a group of Phong triangles stored in a file.
- torus open [... data] out_radius in_radius start_angle end_angle
[out_samples in_samples] - an open torus.
- Examples of opened objects:
- Finally there are instructions that allow the creation
of complex objects:
- csg operation [... data] begin - begin of a CSG operation.
The type of operation may be union, intersection or subtraction. A CSG
(Constructive Solid Geometry) is a binary operation performed on two
object operands (which may also be CSG's).
- csg next - this instruction separates the definition of the
left (first) operand of the CSG from the right (second) operand.
- csg end - this instruction terminates the CSG.
- Examples of CSG objects:
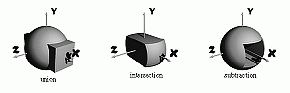
- There is also one instruction that joins several
simple objects into a
primitive object. This is mandatory for CSG or else errors will appear in
the picture:
- list [... data] begin - start of a list of objects, at least two.
- list end.
- This instruction must be used in a CSG context when at least one of the
operands is composed of opened objects (please note that each CSG operand
must bound a finite volume). Example:
list surface matte brown begin ; a new object similar to a pencil
cylinder open 0 -1 0 0 1 0 0.3
cone open 0 1.3 0 0 1 0 0.3
sphere 0 -1 0 0.3
list end
- A transformation is an operation that modifies the geometry of an
object. Normally, transformations are concatenated to previous
transformations, although it is possible to do it in other ways.
- transform none - discards all previous transformations.
- transform scale factor [factor factor] - scaling transformation.
- transform translate point - translation.
- transform rotate x angle - rotation about the X axis (angle in degrees).
- transform rotate y angle.
- transform rotate z angle.
- transform rotate vector angle - rotation about an axis
passing through origin.
- transform general point point point [point] - any
transformation matrix (3x3 or 4x4).
- A texture modifies in some extent the characteristics of a surface. It
is possible to apply transformations to textures and even keep them
independent from object transformations.
- texture none - discards all previous texture transformations.
- texture scale factor [factor factor].
- texture translate point.
- texture rotate x angle.
- texture rotate y angle.
- texture rotate z angle.
- texture rotate vector angle.
- texture general point point point [point].
- texture local - generate all the necessary texture
transformations to access objects without considering their previously
defined object transformations. The keyword invariant is also
accepted.
- Example:
sphere
transform scale 0.2 1 2
transform rotate y ANGLE ; ANGLE is defined elsewhere
texture local
blotch 0.5 surface matte yellow
surface matte red
data 0 0 0 1
- When generating animations, for example, it is important that textures
stick to objects independently of their position, scale, etc or else it
will produce a undesirable effect. If ANGLE varies from 5 to 30 degrees,
the texture still applies correctly to the object and does not float
strangely.
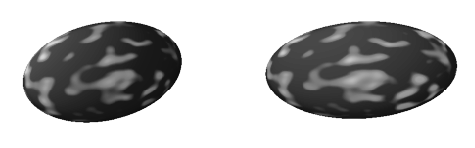
- The available textures are:
Name Parameters
------------------------------------------------------
checkers surface [transform]
blotch scale surface [filename] [transform]
bump scale [transform]
marble [filename] [transform]
fbm offset scale omega lambda threshold octaves [transform]
fbmbump offset scale lambda octaves [transform]
wood color [transform]
round scale [transform]
bozo turbulence [filename] [transform]
ripples frequency phase scale [transform]
waves frequency phase scale [transform]
spotted [filename] [transform]
dents scale [transform]
agate [filename] [transform]
wrinkles scale [transform]
granite [filename] [transform]
gradient turbulence direction [filename] [transform]
imagemap turbulence mode axis filename [transform]
gloss scale [transform]
bump3 scale size [transform]
------------------------------------------------------
- Examples:
sphere round 0.5 data 0 0 0 0.5
sphere bump 0.7 scale 20 data 0 1 0 0.5 ; scale of bump is smaller
sphere bump3 0.5 0.5 scale 1 4 1 data 0 -1 0 0.5 ; strange!
|